| TIME | EVENT |
COMMENTS | DRAWING
|
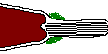
| -30s | Acrosome | The sperm acrosome reacts with the egg jelly causing the acrosome reaction.
|  |
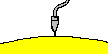
| 0 | Binding | The acrosome reacted sperm binds with the egg. This causes an electrical change in the egg helping prevent other sperm from binding.
|  |
| 30s | Fusion | The successful sperm's membrane fuses with the egg's plasma membrane
|  |
| 1-2m | Cortical Rx | The cortical granules release causing the fertilization membrane to rise, also helping to prevent further sperm entry.
|  |
| 5m | Fertilization Cone | A cone of actin forms around the sperm nucleus, pulling it into the egg.
|  |
| 10-15m | Nuclei Fuse | The sperm and egg haploid nuclei fuse to become a diploid sea urchin nucleus
|  |
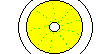
| 20-30m | Centering | The beginnings of the mitotic spindle force the nucleus into the center of the embryo
|  |
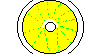
| 50-60m | Streak | The centrosome replicates causing a spread of microtubules resembling a clear streak.
|  |
| 80-90m | Metaphase | The chromosomes line up in the center of the embryo ready for cell division.
| 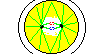 |
| 90-120m | First Division |
Cytokinesis, cell division occurs. The embryo becomes 2 cells.
| 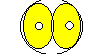 |



















